When it comes to Pre Workout ingredients, it really is quality over quantity.
Anyone can throw caffeine at a problem when they need energy, but too much of it can cause side effects and drowsiness.
For a fully satisfying workout you need more than caffeine, you need an entire arsenal of nutrients that all improve your performance in various ways.
We’ve compiled a list of the best ingredients you can hope to find in a pre workout, how much you should be looking for in each serving, and how it works.
This is what you need to know:
How do Pre Workout ingredients work?
A good pre workout has numerous functions when it comes to getting you ready for a session – these are the main 4 you’ll come across.
- Energy – Stimulants in pre workouts help promote overall energy levels. This keeps you training at full intensity longer than you would normally.
- Focus – Some of the nutrients used by pre workouts are cognitive enhancers. These supply your brain with stronger neurotransmitters which can increase overall focus,, mood and many more.
- Strength – Usually requiring stimulants, pre workouts also have the ability to boost your power output. By stimulating your nervous, these supplements can make stronger connections between your brain and your muscles, allowing you more explosive power.
- Muscle Pumps – This is all about your workout experience. Using vasodilators, pre workouts can dramatically improve blood flow to your muscles – giving you a much larger pump and a more satisfying workout.
There are many nutrients that claim to have these properties, but not a lot that actually deliver on them.
Below we’ll cover certain warning side you should look out for to make sure your chosen supplement is up to industry standards.

Skip to the Top 3 Pre Workouts that contain the best ingredients.
What makes a Bad Pre Workout?
Poor Nutrient Transparency.
With any supplement, the first thing you should inspect is the ‘supplement facts’ label on the back. This will give you the run-down on every ingredient the manufacturer used to put the product together.
However, some reveal more than others – and one of the main features you should stay wary of, are proprietary blends.
What are Proprietary Blends?
You’ll have seen these before – but they’re easy to miss.
Proprietary blends are when supplement companies group ingredients together, and hide individual doses.
You’ll know what’s in the supplement you’re taking, what you won’t know is how much, this could lead to one of either two problems:
- The supplement is under-dosed – The more common problem. Hidden dosages allow companies to cut corners on the amount they use.
- It’s overdosed and potentially dangerous – This is when companies want to get you wired, they want you to have a good session so you buy their product again. What they’re not telling you, is the risk you’re taking to get there.
An example proprietary blend:

This is a classic example. We know what’s in this product – what we don’t know, is how much.
And supplement companies do this all the time – especially with pre workouts.
What are the best Pre Workout Ingredients?
After doing the necessary research, we’ve found four main categories of pre workout nutrients that help promote all of the above mentioned benefits.
These are:
- Strength Support – Increasing overall power output.
- Energy Boosters – Maintain intensity throughout your session.
- Cognitive Enhancers – Improving focus and mental ability.
- Vasodilators – Enhancing blood flow and muscle pumps.
Some of these nutrients do overlap with one another – you can learn all the main effective choices below:
Caffeine (Recommended Dosage: 100 – 200mg)
Arguably one of the best stimulants on the market. Caffeine adds numerous levels to your workout that ensures a good session.
By blocking adenosine – a brain chemical that promotes sleep, caffeine ensures you are more wakeful and energetic while it is in effect.

The main benefits of Caffeine:
- Running Capacity – Studies have shown that taking caffeine before aeorbic exercise can dramatically increase your performance. [1]
- Power Output – Caffeine also promotes neuromuscular performance in seasonsed weight lifters. [2]
- Adrenaline – For that added umph, caffeine can also help your body have a more accessible supply of adrenaline. [3]
- Reaction Time – Subjects that have supplemented caffeine in studies have seen an increase in mental reaction and processing speeds. [4]
- Blood Flow – There is minor evidence that caffeine can also promote blood flow in sonme subjects. [5]
- Thermogenic Fat Burning – Studies have also shown that ingesting caffeine can lead to an increase in fat loss by thermogenesis. A process that raises body heat provoking a calorie burning cool-down effect. [6]
Quick note about Caffeine:
Some companies believe they can just throw caffeine at their product to make it effective.
Used properly, you don’t need as much caffeine as most brands make out. As long have you more than just caffeine for boosting energy in your pre workout, you’ll have a strong experience.
If it’s combined with L-Theanine this is usually a good sign.
L-Theanine (Recommended Dosage: 100 – 200mg)
An amino acid that is known for it’s ability to promote stress relief and relaxation. So why do you want it in your nootropic?
Because it makes caffeine amazing. This nutrient works incredibly well with this stimulant – so much so that this combination is referred to in the world of nootropics as ‘smart-caffeine’. The overall result is heightened attention and focus.

The main benefits of L-Theanine:
- Calmness and Focus – When compared to a placebo, subjects that have used L-Theanine have been reported to be significantly more relaxed and tranquil. [7]
- Increased Reaction Time and Attention – After being combined with caffeine, L-Theanine has been seen to deliver alertness, reaction time and overall better attention span compared to those just using caffeine. [8]
- Reduces Anxiety – L-Theanine has also been seen to help with the reduction of anxiety. In a study involving a stressful situation, subjects using this amino acid had approximately half the anxiety of those taking a placebo.
Quick note about L-Theanine:
Although it has its merits, you’re going to get the most benefit out of L-Theanine if it’s combined with caffeine.
This ensures you get that perfect balance between energy and focus to hone in your training and get the best out of your workout.
Citrulline Malate (Recommended Dosage: 5000 – 8000mg)
Extracted from Watermelons, Citrulline Malate is a natural amino acid that dramatically improves muscle pumps.
Converted by your liver into L-Arginine, Citrulline Malate increases your body’s overall levels of nitric oxide. It’s a vasodilator – meaning it relaxes your blood vessels and allows so more can pass through it. This is great for muscle pumps, but it also has various other benefits:

The main benefits of Citrulline Malate
- Fights Fatigue and increases Endurance – Studies have shown that regular supplementation of Citrulline can reduce fatigue, delaying tiredness and allowing subjects to produce more reps. [9]
- Reduces Muscle Soreness – Reports also show that supplementing Cirtulline for sport can reduce overall muscle soreness. [10]
- Dramatically Dilates Blood Vessels – By increasing your body’s nitric oxide, your blood vessels can hold more volume and give you incredible muscle pumps. [11]
Quick note about Citrulline Malate:
You need a lot of it. If you see a pre workout that uses less than 4g of this stuff, you’re probably not going to get much benefit at all. 5 – 8g is the gold standard. This will give you a massive surge in blood flow and some monstrous pumps.
Secondly, ignore supplementing L-Arginine. People think as Citrulline is converted into L-Arginine in your body that it’s a fast-track to a serious pump – it’s not. Supplementing it raw is incredibly hard for your body to absorb, resulting in very little effect.
Creatine Monohydrate (Recommended Dosage: 1000 – 5000mg)
One of the better ingredients for boosting performance and overall energy levels. Found commonly in meats, eggs and fish, creatine has been linked to promoting health in the brain, bones and muscles.
There are so many benefits that creatine to add to your workout experience, here are just a few of the main points:

The main benefits of Creatine Monohydrate:
- Increases Overall Power Output – It’s been well established over numerous studies that creatine dramatically improves strength and power output. [12]
- Running Capacity – With regular supplementation, Creatine has been seen to increase overall endurance in several sports. [13]
- Gaining Lean Mass – Supplementing Creatine can also help you pack on more muscle mass with resistance training compared to training without it. [14]
- Boosts Blood Flow – Studies have shown that regular supplementation of creatine can lead to improved blood and muscle pumps while training. [15]
Quick note about Creatine Monohydrate:
Creatine works best when you have a regular supply of it in your diet. Most companies recommend a loading phase for the best results.
On it’s own, creatine is relatively cheap – stacking creatine monohydrate outside of your preworkout could help you get the most benefit – so if it does contain it, you’ll get the full experience.
Beet Root Extract (Recommended Dosage: 250 – 500mg)
An unlikely choice of pre workout is definitely beetroot extract – but don’t be fooled. It’s incredibly effective.
Full of nitrate, Beet Root has been seen to promote physical performance in athletes, along with a few other benefits. Here are the main things you need to know about this extract:

The main benefits of Beet Root Extract:
- Increases Exercise Endurance – Studies have shown athletes that drank 490ml of Beetroot juice, saw a 4.2% increase in performance, relative to the placebo group. [16]
- Energy Efficiency – It has also been reported that Beet Root reduces the oxygen cost of exercise while also improving performance. It makes you more efficient while working out. [17]
It’s a great raw and natural addition to any pre workout.
L-Carnitine (Recommended Dosage: 500 – 2500mg)
A good, reliable amino acid that helps with various functions throughout the body, many of which we can take advantage of as a pre workout.
Found mainly in animal products, here are the main benefits you can expect from supplementing this amino acid:

The main benefits of L-Carnitine:
- Lowers Fatigue – Studies have have shown that supplementing Acetly-L Carnitine can help reduce both mental and physical fatigue. [18]
- Lessens Muscle Damage and Soreness – Finding in experienced weight lifters discovered that supplementing L-Carnitine can reduce overall muscle damage and soreness after training. [19]
- Increases Running Capacity – Subjects in studies supplementing Carintine for energy found that they had more efficient energy production that the placebo group when exercising. [20]
- Enhances Attention and Focus – It has also been known that L-Carnitine can also help with increase with improving attention and focus. This can help you to continue supplying high quality reps at the gym. [21]
Quick Note about L-Carnitine
Always check the dosage. You need a large amount of L-Carntine to get the benefits – and a lot of supplements are going to sell you short. They’ll preach the advantages of this amino acid, but contain nowhere near enough of it to give you the full experience.
Make sure you’re getting at least 500mg of this nutrient per serving for the full advantage.
Skip to the Top 3 Pre Workouts that contain the best ingredients.
What are the Worst Pre Workout Ingredients?
If you’ve read that list and you haven’t found a common pre workout ingredient you’re looking for it’s either:
- Not as good as the ones that we’ve covered
Or
- One of the worst pre workout ingredients
This part of the guide outlines the more common ingredients that you don’t want in a pre workout, and why they’re bad.
Here’s out shortlist:
Ingredients You Should Avoid
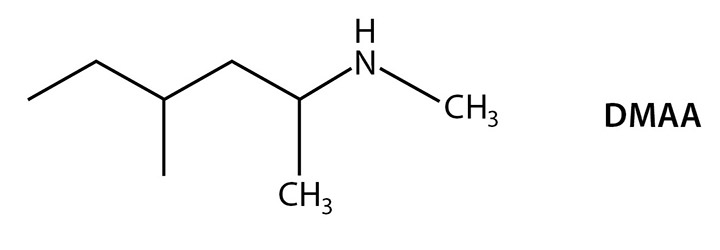
DMAA
Made famous by its addition to Jack3d – a pre workout supplement that led to numerous health complications.
DMAA is 1,3-Dimethylamylamine – although thought to be banned in the supplement industry, you can still come across it if you are not careful.
Structurally similar to amphetamines and works in a similar way, there are numerous cases of DMAA causing harm on both minor and critical levels.
The side effects of this ingredient include:
- High Blood Pressure
- Glaucoma
- Irregular Heartbeat
- Increased risk of heart attack and/or stroke
It’s definitely not a good option – especially if it’s in a proprietary blend. You don’t need much DMAA to have a problem, so it’s useful to know just how much you’re actually getting.

Synephrine
Also known as Bitter Orange Extract, Synephrine is a natural stimulant and fat burner, that could also cause side effects.
This goes double when taken with caffeine – the two have been known to cause serious problems when taken together.
Here’s what you could be in for when supplementing synephrine:
- Elevated Hearth Rate
- Headaches
- Increased risk of heat attack and/or stroke
- Raise blood pressure
Essentially, the side effects are similar to that of DMAA – the difference here is that Synephrine is still widely available in supplements.
A pre workout isn’t the only place you’ll find synephrine either. It appears regularly with caffeine in numerous fat burners. Make sure you do your research before you purchase.

Beta-Alanine
The views on Beta-Alanine are mixed. The studies are pretty conclusive – it does deliver on it’s effects. Beta-Alanine is good for buffering the acid in your muscles and giving you a better performance in the gym.
But it does come at a cost.
Studies have shown Beta-Alanine can lead to temporary paresthesia. A condition where the skin on your face and hands becomes incredibly itchy and tingles.
The effect is harmless, but the distraction that this can cause, especially when you’re dealing with heavy weight, can easily throw you off your game.
It’s definitely worth keeping your eye on.
Which Pre Workouts Contain the Best Ingredients?
We’ve done the research, and examined numerous of the most popular and highest rated pre workouts on the market. After checking their nutrient profile, dosage, safety and overall effectiveness – we’ve got it down to three.
If you’re in the market for a reliable pre workout, we suggest you start there.
– See Our Top 3 Pre Workouts –
References:
[1] Schneiker KT1 Bishop D, Dawson B, Hackett LP., Effects of caffeine on prolonged intermittent-sprint ability in team-sport athletes., Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006 Mar;38(3):578-85.
[2] Mora-Rodríguez R, García Pallarés J, López-Samanes Á, Ortega JF, Fernández-Elías VE., Caffeine ingestion reverses the circadian rhythm effects on neuromuscular performance in highly resistance-trained men., PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033807. Epub 2012 Apr 4.
[3] Norager CB, Jensen MB, Weimann A, Madsen MR., Metabolic effects of caffeine ingestion and physical work in 75-year old citizens. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study., Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006 Aug;65(2):223-8.
[4] Hunt MG, Momjian AJ, Wong KK., Effects of diurnal variation and caffeine consumption on Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA) performance in healthy young adults., Psychol Assess. 2011 Mar;23(1):226-33. doi: 10.1037/a0021401.
[5] Shechter M, Shalmon G, Scheinowitz M, Koren-Morag N, Feinberg MS, Harats D, Sela BA, Sharabi Y, Chouraqui P., Impact of acute caffeine ingestion on endothelial function in subjects with and without coronary artery disease., Am J Cardiol. 2011 May 1;107(9):1255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.12.035. Epub 2011 Feb 23.
[6] Kim TW, Shin YO, Lee JB, Min YK, Yang HM., Caffeine increases sweating sensitivity via changes in sudomotor activity during physical loading., J Med Food. 2011 Nov;14(11):1448-55. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2010.1534. Epub 2011 Sep 1.
[7] Lu K, Gray MA, Oliver C, Liley DT, Harrison BJ, Bartholomeusz CF, Phan KL, Nathan PJ., The acute effects of L-theanine in comparison with alprazolam on anticipatory anxiety in humans., Hum Psychopharmacol. 2004 Oct;19(7):457-65.
[8] Haskell CF, et al The effects of L-theanine, caffeine and their combination on cognition and mood . Biol Psychol. (2008)
[9] Bendahan D, Mattei JP, Ghattas B, Confort-Gouny S, Le Guern ME, Cozzone PJ., Citrulline/malate promotes aerobic energy production in human exercising muscle., Br J Sports Med. 2002 Aug;36(4):282-9.
[10] Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM., Citrulline malate enhances athletic anaerobic performance and relieves muscle soreness., J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181cb28e0.
[11] Sureda A, Córdova A, Ferrer MD, Pérez G, Tur JA, Pons A., L-citrulline-malate influence over branched chain amino acid utilization during exercise., Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 Sep;110(2):341-51. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1509-4. Epub 2010 May 25.
[12] Rahimi R., Creatine supplementation decreases oxidative DNA damage and lipid peroxidation induced by a single bout of resistance exercise., J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Dec;25(12):3448-55. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182162f2b.
[13] Okudan N, Gokbel H., The effects of creatine supplementation on performance during the repeated bouts of supramaximal exercise., J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2005 Dec;45(4):507-11.
[14] Candow DG, Chilibeck PD, Burke DG, Mueller KD, Lewis JD., Effect of different frequencies of creatine supplementation on muscle size and strength in young adults., J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jul;25(7):1831-8. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181e7419a.
[15] Sanchez-Gonzalez MA, Wieder R, Kim JS, Vicil F, Figueroa A., Creatine supplementation attenuates hemodynamic and arterial stiffness responses following an acute bout of isokinetic exercise., Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011 Sep;111(9):1965-71. doi: 10.1007/s00421-011-1832-4. Epub 2011 Jan 20.
[16] Wylie LJ, et al., Dietary nitrate supplementation improves team sport-specific intense intermittent exercise performance . Eur J Appl Physiol. (2013)
[17] Vanhatalo A, et al Acute and chronic effects of dietary nitrate supplementation on blood pressure and the physiological responses to moderate-intensity and incremental exercise . Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. (2010)
[18] Malaguarnera M, Gargante MP, Cristaldi E, Colonna V, Messano M, Koverech A, Neri S, Vacante M, Cammalleri L, Motta M., Acetyl L-carnitine (ALC) treatment in elderly patients with fatigue., Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008 Mar-Apr;46(2):181-90. Epub 2007 Jul 20.
[19] Volek JS, Kraemer WJ, Rubin MR, Gómez AL, Ratamess NA, Gaynor P., L-Carnitine L-tartrate supplementation favorably affects markers of recovery from exercise stress., Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Feb;282(2):E474-82.
[20] Wall BT, Stephens FB, Constantin-Teodosiu D, Marimuthu K, Macdonald IA, Greenhaff PL., Chronic oral ingestion of L-carnitine and carbohydrate increases muscle carnitine content and alters muscle fuel metabolism during exercise in humans., J Physiol. 2011 Feb 15;589(Pt 4):963-73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.201343. Epub 2011 Jan 4.
[21] Van Oudheusden LJ, Scholte HR., Efficacy of carnitine in the treatment of children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder., Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2002 Jul;67(1):33-8.
